Researchers Reveal Mechanism Regulating Rhodium Migration and Size Redistribution in Rhodium Catalysts
The migration of Rh atoms under a gas/reactive environment is important for the dynamic restructuring and size redistribution of Rh catalysts in a variety of structure-sensitive catalytic reactions.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. ZHANG Tao and Assoc. Prof. YANG Bing from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. ZHOU Si from the Dalian University of Technology, revealed a controlled-release mechanism to regulate Rh atom migration through two-dimensional (2D) zeolite nanosheets (ZSM-5-2D).
This study was published in ACS catalysis on January 5.
Dynamic aggregation/redispersion of Rh catalysts in/out of the ZSM-5-2D (Image by YANG Bing)
"The migration rate of Rh atoms can be precisely controlled by regulating the mutual interaction of the gas environment and support confinement, enabling a quasi-continuous size control over a wide range from single atom to nanoparticle reversibly," said YANG.
Through a variety of state-of-the-art in-situ characterizations, the researchers directly observed the dynamic aggregation/redispersion of Rh catalysts in/out of the ZSM-5-2D, enabling a quasi-continuous size control over a wide size range from Rh single atom to Rh nanoparticle reversibly.
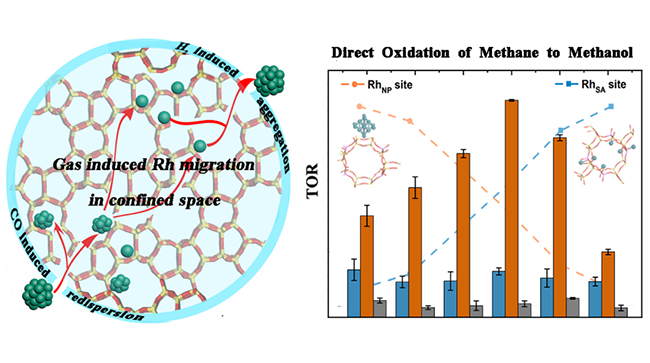
The catalytic testing for mild oxidation of methane disclosed that the sub-nanometer Rh nanoclusters (RhNC) accounted for the highest methanol activity of 39.7 molCH3OOH·molRh-1·h-1 with a remarkable selectivity as high as 73.2%, far beyond that of single atom species and larger particles.
Density functional theory calculations and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy further elucidated the size dependency by examining the formation of ·OH radicals for methane oxidation.
"This work reveals a controlled-release mechanism in zeolite encaged Rh catalyst, which is inspiring for the design of atomically precise catalysts," said YANG.
The above work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, the CAS Project for Young Scientists in Basic Research, and the Innovation Grant from DICP.