Study Explores Dosage-effectiveness of Modified Clay Flocculating Red Tide Organisms
Red tide is a global marine ecological disaster, and its frequency, intensity, and geographic extent have increased worldwide in recent years. Currently, the main remediation technology employed for red tides control on a large scale is to spray modified clay (MC) on the surface of red tides-affected water.
However, the spraying dosage of MC usually was judged only by previous spraying experience, which cannot guide the application of MC well.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. YU Zhiming from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) revealed mechanical mechanism of MC dosage impacting its effectiveness, and preliminarily established dosage-effectiveness mathematical model of MC flocculating red tide organisms.
The study was published in Separation and purification technology on Oct. 22.
Researchers found that when using MC to flocculate red tide organisms, with an increasing dosage of MC, the effectiveness of MC for microalgae removal increased first and then decreased. The attractive total interaction energy between MC and MC at close range caused self-flocculation of MC in seawater, which decreased its effectiveness for microalgae removal. MC dosage changed self-flocculation proportion of MC by affecting efficient collision between MC and MC, and between MC and microalgae cells.
Moreover, a mathematical model established based on the extended Langmuir model can simulate dosage-effectiveness of MC well, and the quantitative relationship between the dosage of MC and its degree of self-flocculation was deduced based the mathematical model.
"The spraying method of MC strongly affected its effectiveness, and dosage-effectiveness mathematical model established in the study can be used as an important reference for MC dosage optimization strategy," said ZANG Xiaomiao, first author of the study.
"The study will help to enrich particle flocculation theory and guide efficient spraying practices of MC technology for red tides control," said Prof. YU, the corresponding author.
This study was supported by the Marine S&T Fund of Shandong Province for Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, etc.
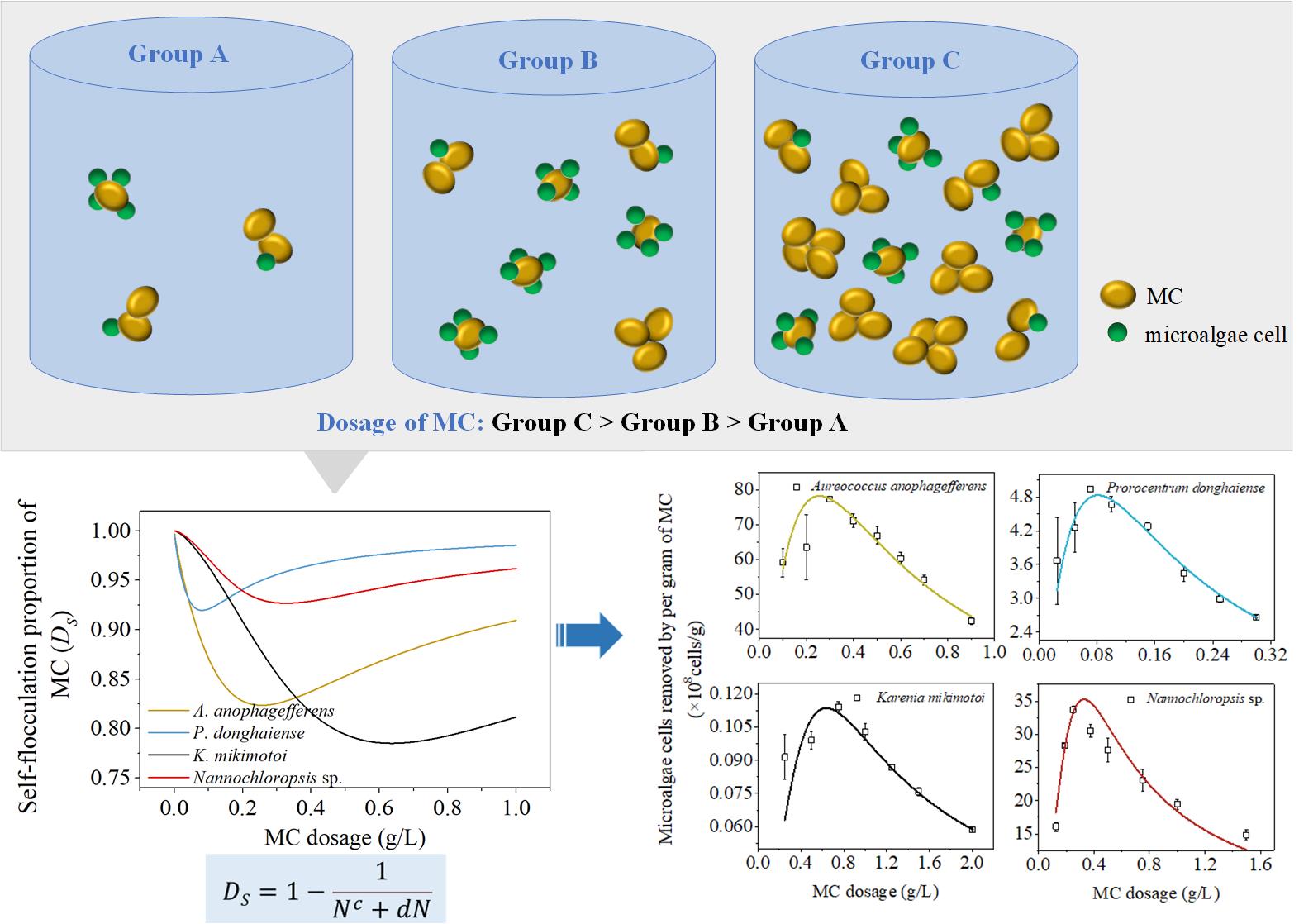
Schematic illustration of influence of MC dosage on microalgae removal
Xiaomiao Zang, ZhimingYu, Wenbin Jiang, Xiuxian Song, Xihua Cao. (2022). Dosage-effectiveness of modified clay flocculating red tide organisms: mechanical mechanism and mathematical model. Separation and Purification Technology.
(Text by ZANG Xiaomiao)
Media Contact:
ZHANG Yiyi
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: zhangyiyi@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)