Scientists First Raise Sustainable Diffusion Source to Fabricate Anticorrosion Metallic Coatings
Magnesium and magnesium alloys have high strength/weight ratios and are frequently utilized in various structures to reduce weight. However, due to the activity of Mg, magnesium alloys are prone to be corroded in marine atmosphere.
The powder thermal diffusion alloying method, or pack cementation, is frequently employed to enhance the corrosion resistance of magnesium alloys. Traditionally, it is crucial to change the diffusion source between two successive pack cementation processes.
Recently, the research team led by Prof. HUANG Yanliang from the Institute of Oceanology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOCAS) raised a new diffusion source that could be utilized in multiple pack cementation processes, which means that it's a recyclable diffusion source.
The study was published in Journal of Cleaner Production on Feb. 23.
Researchers found the recyclable diffusion source based on thorough investigation on the evolution of a diffusion source in powder thermal diffusion alloying processes.
The recyclable character of this diffusion source is mainly attributed to reversible chemical reactions related to a compound called zinc hydroxide chloride. When heated, the compound will decompose, and active metal ions will emerge. Upon cooling, zinc hydroxide chloride will form again. Then a cycle formed.
"This cycle indicates that the diffusion source could be utilized repeatedly for coating fabrication on magnesium alloys," said Dr. LU Dongzhu, first author of the study.
"Between two adjacent pack cementation processes, there is no need to change the diffusion source for a new one or add other materials into the diffusion source," said Prof. HUANG.
The recyclable feature of zinc hydroxide chloride has been confirmed further by a series of experiments in this study. Promotion of such a recyclable diffusion source would save materials effectively in the pack cementation industry.
"Meanwhile, due to the omitted reloading of powders between two adjacent pack cementation processes, the environment and the health of related workers can be protected," said Dr. LU.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Exploring Key Scientific Instrument, the Nantong Science and Technology Development Funds, and the Central Government Guiding Funds for Local Science and Technology Development.
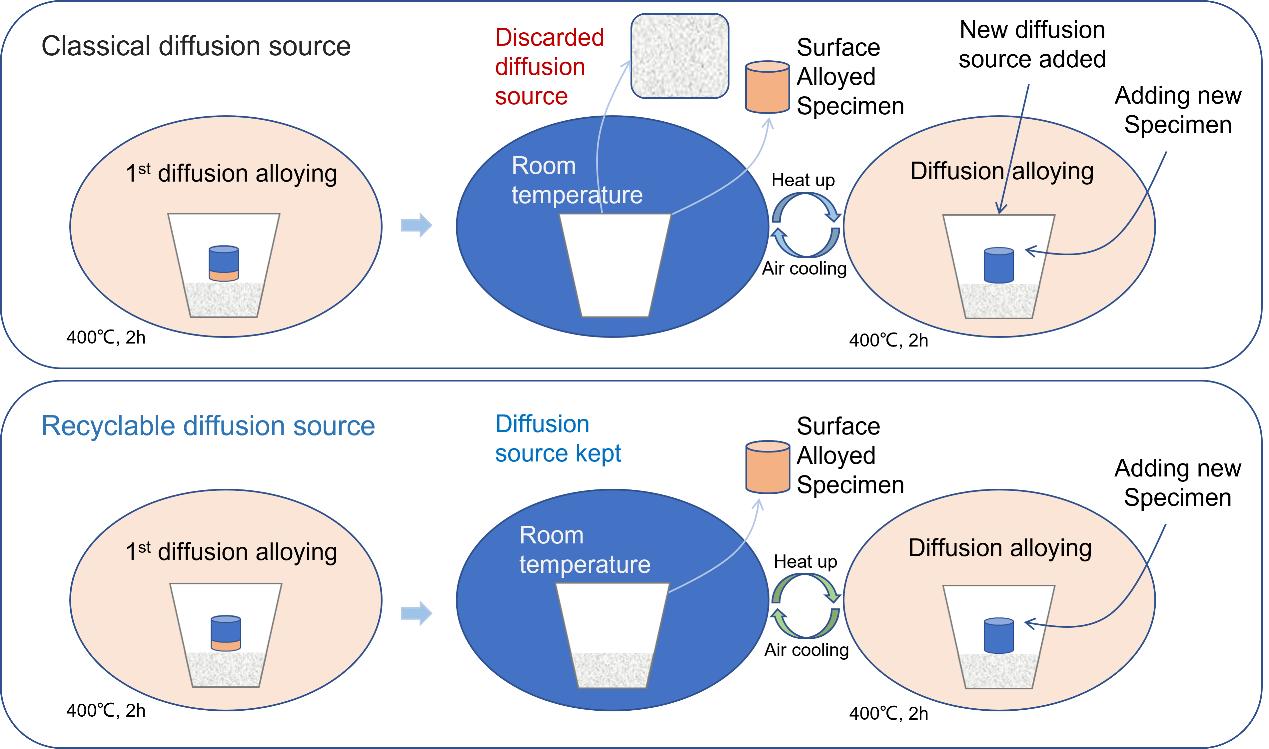
Comparation of the utilization of the classical diffusion source and the recyclable diffusion source
Dongzhu Lu*, Quantong Jiang, Xiumin Ma, Liang Fan, Yanliang Huang*, Baorong Hou. (2022). Zinc chloride hydroxide - A recyclable diffusion source for fabrication of zinc rich coatings on magnesium alloys. Journal of Cleaner Production, 344: 131066.
LU Dongzhu
Institute of Oceanology
E-mail: ldz@qdio.ac.cn
(Editor: ZHANG Yiyi)