Construction and Application of Electrocoagulation and Filtration Linkage Control System in Recirculating Aquaculture System
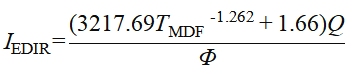
When the aquaculture water was treated using an electrocoagulation diameter increasing reactor (EDIR) for 2 min, with current density at 50 A/m2 and influent flow at 300 L/h, the D50 of TSS increased by 86.43%.
In addition, results showed that the EDIR-MDF linkage control system increased the average removal efficiency of RAS for TSS, chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia, and nitrite by 24.07%, 24.30%, 8.94%, and 1.39%, respectively, and resulted in average energy consumption and anode loss of EDIR of 2.38 kWh/d (1.68 RMB/d) and 370 g/d (2.22 RMB/d). EDIR-MDF linkage control system can significantly increase the water quality of the aquaculture pond.
The work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the Science and Technology Major Project of Guangxi, the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation.
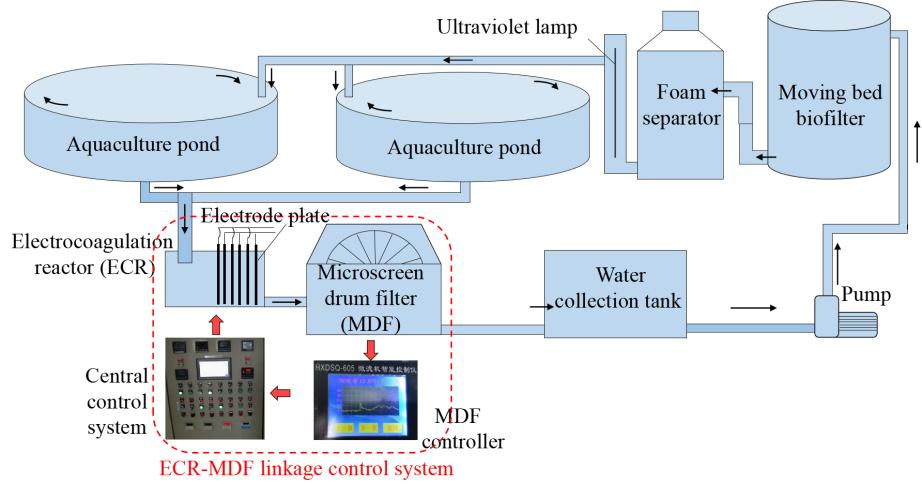
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of the experimental system
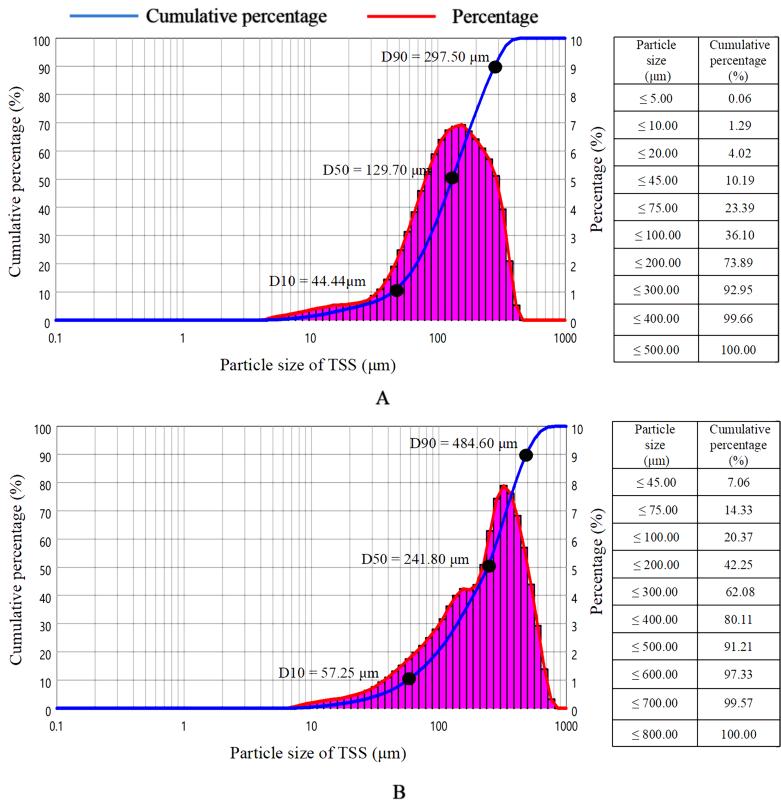
Fig. 2 Comparison of TSS particle size between influent (A) and effluent (B) of EDIR in the laboratory-scale system
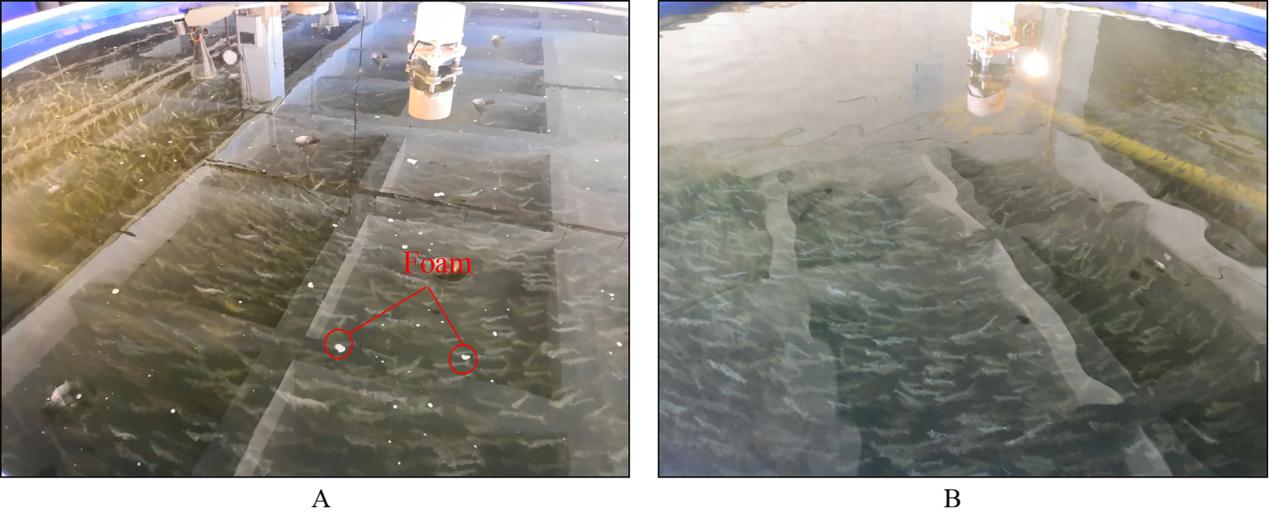
Fig. 3 Pictures of aquaculture pond in no-EC stage (A) and EC stage (B)
Xu, J., et al. Construction and application of an electrocoagulation and filtration linkage control system in a recirculating aquaculture system. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2021, 44, 102379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102379.