Scientists Reveal Carbon-carbon Coupling Reaction in Neutral Metal Carbonyls
Metal carbonyls play an important role in heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysis such as Fischer–Tropsch chemistry, hydroformylation, alcohol synthesis, and acetic acid synthesis.
Laser vaporization technique has been successfully employed in generating and studying homoleptic metal carbonyl cations and anions in the gas phase, which serve as archetypical examples for demonstrating the metal–ligand bonding and the electron counting rules. However, the spectroscopic characterization of neutral metal carbonyls in the gas phase are significantly more challenging due to the difficulty of size selection.
A research team led by Prof. JIANG Ling from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. ZHOU Mingfei from Fudan University, identified a carbon-carbon coupling reaction in neutral transition metal carbonyls.
Their findings, published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, revealed that the C-O bond breaking and C-C bond formation proceed efficiently in the reactions between laser vaporized titanium atoms and carbon monoxide and also highlighted a viable strategy for CO insertion for carbon-chain growth and higher alcohol synthesis.
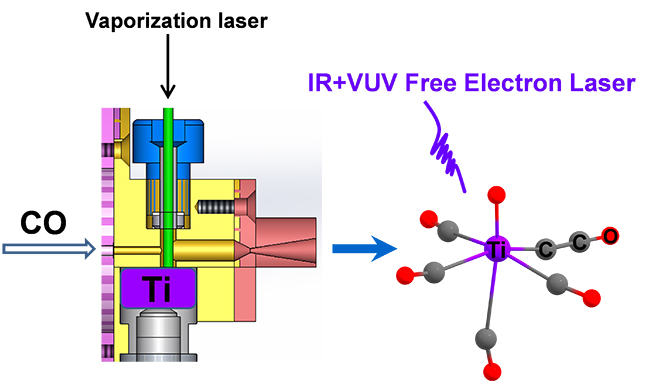
Observation of Carbon–Carbon Coupling Reaction in Neutral Transition-Metal Carbonyls (Image by WANG Chong)
Based on the recently-developed infrared plus vacuum ultraviolet (IR+VUV) two-color ionization spectroscopy using a tunable vacuum ultraviolet free electron laser (VUV-FEL), the researchers synthesized and characterized a series of neutral titanium carbonyl complexes.
Infrared spectroscopy in conjunction with quantum chemical calculations confirmed that the complexes with chemical formula of Ti(CO)n (n = 4-7) all had unexpected titanium ketenylidene OTiCCO(CO)n-2 structures, demonstrating that the C-O bond breaking and C-C bond formation proceed in the reactions between laser vaporized titanium atoms and carbon monoxide.
Bonding analysis indicated that the OTiCCO core structure could be described by the bonding interactions between a TiO+ cation in the doublet ground state and a doublet ground state of CCO-.
Theoretical calculations predicted that the Ti + nCO→OTiCCO(CO)n-2 reactions were both thermodynamically exothermic and kinetically facile in the gas phase. The observed C-O bond cleavage and C-C bond formation was a viable strategy for CO insertion for carbon-chain growth and higher alcohol synthesis.
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
457 Zhongshan Road, Dalian, 116023, China
Tel: 86-411-84374221
E-mail: wangyj@dicp.ac.cn