Exposure to pathogens in recreational, or drinking water is a serious public health concern. Therefore, it is important to rapidly determine and identify trace levels of pathogens in real environmental samples. Recently, the development and applications of biosensors for rapid and sensitive detection of bacterial cells have attracted considerable attention.
Research group of Marine Environmental Electrochemistry and Sensing Technology cooperated with the group of Environmental Microbiology Research to develop a label-free potentiometric aptasensor for rapid, sensitive and selective detection of bacteria in costal seawater. In their previous research, they developed a label-free potentiometric aptasensing concept to monitor small analytes in a homogenous solution (Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84, 2055-2031). In the present research, a label-free potentiometric aptasensor for rapid, sensitive and selective detection of Listeria monocytogenes (LM), a pathogen widely distributed in the environment was developed. An aptamer binds specifically to internalin A, a surface protein present in LM cells was used as a bioreceptor. Protamine, a group of arginine-rich polycationic proteins extracted from the Salmonidae fish family, is selected as an indicator for the transduction of potential signal. Using this method, LM can be detected down to 10 CFU mL-1. Coupled to an online filtration system, the bioassay has been evaluated with spiked coastal seawater samples and shows good recovery and high accuracy.
The results have been published on Analytical Chemistry, (Ding et al., Potentiometric Aptasensing of Listeria monocytogenes Using Protamine as an Indicator. Analytical Chemistry, 2014, DOI: 10.1021/ac502335g).
Link: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac502335g
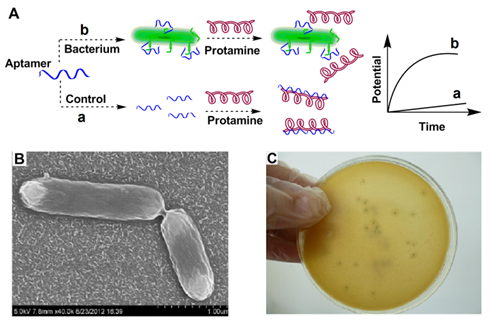
Figure:Schematic illustration of potentiometric aptasensing of Listeria monocytogenes cells using a polycation-sensitive membrane electrode