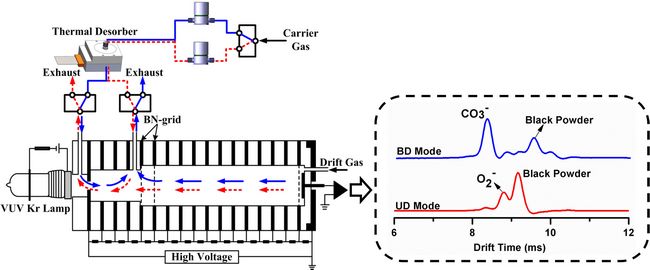
Figure: Schematic diagram of dopant-assisted negative photoionization ion mobility spectrometry with fast switchable CO3- and O2- reactant ions
Recently, Prof. LI Haiyang et al. of DICP developed a dopant-assisted negative photoionization ion mobility spectrometry with fast switchable reactant ions for explosives detection. The accomplishment was published in an article on the Analytical Chemistry. (http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ac404067z)
Ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) has been proved the leading technology for on-site detection of trace amount of explosives due to its many attractive features such as high sensitivity, fast response and portability. However, its application is limited by its high false positive response in complex environments. Thus, improving the accuracy of identification and avoiding the false positive response has became an urgent problem to solve in IMS.
For the detection of explosives by IMS, we observed the different reactant ions often lead to different ionization channels and produce diverse product ions, and the different product ions provide more information. Fast switchable CO3–(H2O)n and O2–(H2O)n reactant ions were realized in a dopant-assisted negative photoionization ion mobility spectrometer (DANP-IMS) in less than 2 seconds by simply changing the gas flow direction. The yields of CO3–(H2O)n and O2–(H2O)n were up to 88% and 89% at the optimal conditions, respectively. Preliminary application for detection of common explosives 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT), cyclo-1,3,5-trimethylene-2,4,6-trinitramine (RDX), ammonium nitrate fuel oil (ANFO), and black powder (BP) showed that the fast switchable CO3–(H2O)n and O2-(H2O)n could provide more information for correct identification of explosives. In addition, the switchable CO3–(H2O)n and O2–(H2O)n reactant ions own the potential for the study of ionization mechanism and comparison of the reactant ion chemistry in IMS.
The development of DANP-IMS with fast switchable reactant ions a new progress based on previous works on DANP-IMS (Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 319-326). (Text by WANG Weiguo/ Photo by CHENG Shasha)
Contact: LI Haiyang
Email: hli@dicp.ac.cn
Tel: 0411-84379510